Table of Contents
Many WordPress websites frequently use APIs to get real-time features like pulling live stock prices, weather updates, syncing product data, or showing social media feeds. When you want to build a dynamic page, knowing WordPress REST API integration can unlock the possibilities.
Here, fetching data from an API is not a real challenge, but how to do it efficiently, securely, and in a way that doesn’t slow down your website. By learning how to fetch data from api, you make your site remain fast, responsive, and reliable.
Depending on your needs, WordPress gives you two flexible options. Use its built-in HTTP API for custom integrations, or choose a plugin that makes wordpress api integration simple through an easy interface.
Once the data is retrieved, you may want to make it searchable, editable, or reusable inside WordPress. That’s where custom fields become useful. The custom fields help in storing and organizing external API data for use anywhere across your site, which is especially handy when working with JSON API WordPress endpoints.
Understanding How to Fetch Data from an API in WordPress
To fetch data from an API and an external source, WordPress provides its own HTTP API. This is a set of PHP functions that make HTTP requests, handle responses, and support all key methods like GET, POST, PUT, and DELETE. So, there are two ways to do it:
- Fetching API data manually using custom code.
- Fetching API data using a plugin.
Here, we only see method 2, Fetching API data using a plugin, as this method is better suited for beginner users.
Fetching Data Using a Plugin
Many plugins can make wordpress connect to external rest api processes easily. For example, the WPGetAPI plugin allows you to connect and display data from any API using a visual interface.
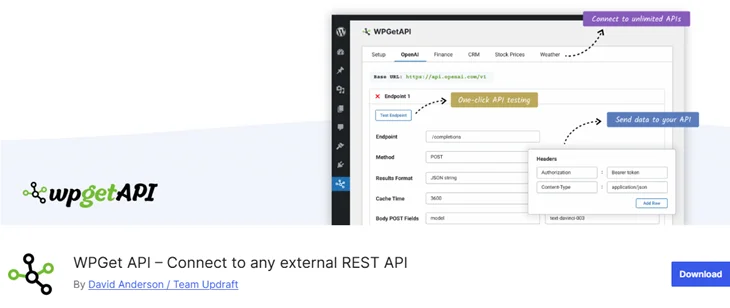
Here’s how to do it:
1. Install and activate the WPGet API plugin.
2. Go to WPGetAPI > Setup in your dashboard.
3. Enter the API name, base URL (https://randomuser.me), and endpoint (/api/).
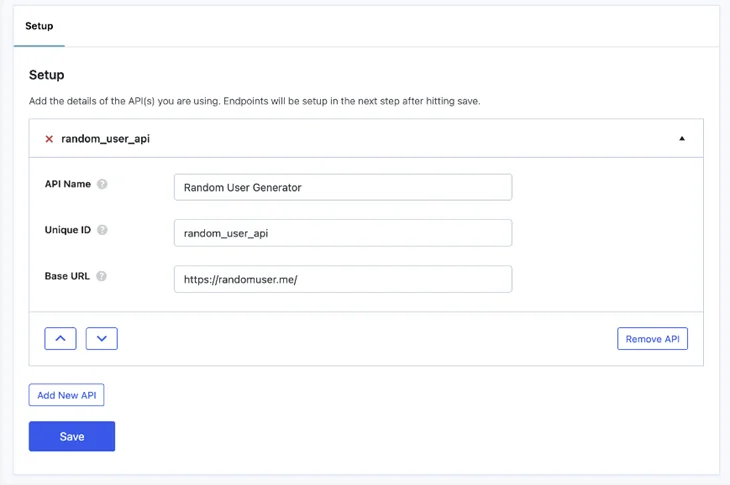
4. Click on the new tab that appears with your API’s name to open its advanced settings.
5. Enter all the details as you need. If you’re not sure, you can leave this as is except for the unique ID (which can be whatever you want) and the endpoint (which should be available from the API docs).
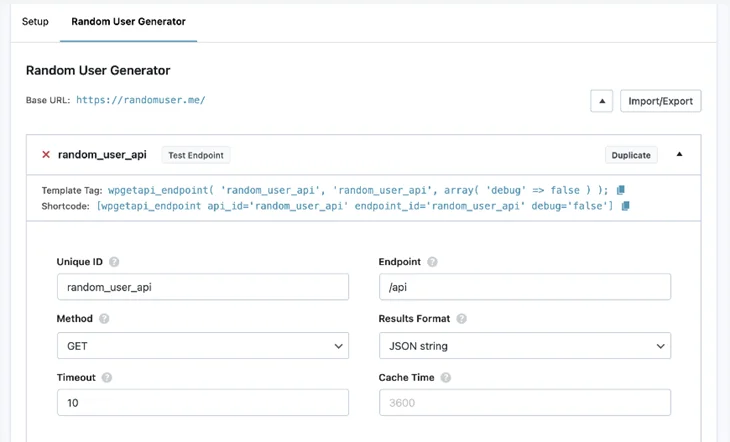
6. Now, click on Test Endpoint to verify that the connection is active. When you should see a success message and some data fetched from the API:
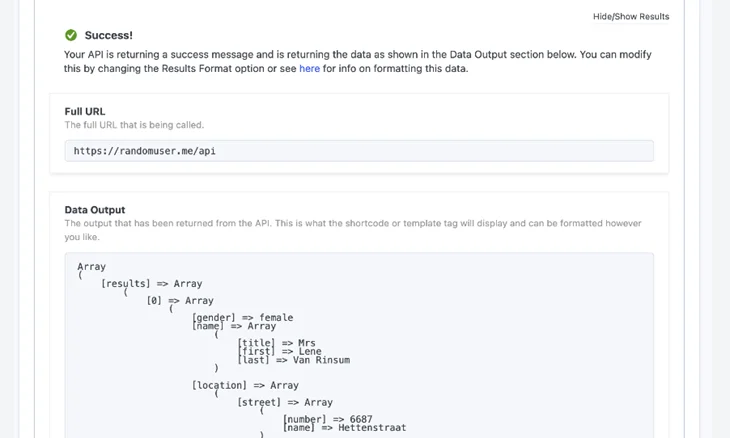
7. Save your settings and test the endpoint. Once confirmed, copy the shortcode the plugin provides and paste it anywhere on your site.
Example shortcode: [wpgetapi_endpoint api_id=’random_user’ endpoint_id=’user_data’]
This plugin automatically fetches and displays API data, giving you a simple WordPress REST API integration without coding. WPGetAPI also supports authentication, caching, and JSON formatting, making it useful for complex or private APIs.
Best Practices for Optimizing API Performance
Fetching data from APIs is a great way to make your website dynamic and more functional, but it must be done carefully to maintain performance and reduce server load.
1. Cache API Responses
Use WordPress caching plugins to temporarily store API data. This reduces unnecessary repeated requests, reduces server load, and makes the site faster.
2. Use Asynchronous Requests
For large APIs or data sets, use background processes or scheduled events to prevent frontend slowdowns.
3. Respect API Rate Limits
Every API provider sets a request limit. Use caching and throttling to avoid exceeding these limits and to avoid getting blocked by the API service.
4. Validate API Responses
Always verify the data structure before saving it. Handle missing or unexpected fields to prevent errors on the website.
5. Secure Your Integrations
Never expose API keys in public code. Use HTTPS and store sensitive credentials in your wp-config.php file or environment variables. This helps keep your API credentials secure and private.
Following these steps ensures your WordPress REST API integration is secure, efficient, and reliable.
Transforming Your WordPress Site with Live API Data
Fetching data from an API in WordPress adds powerful, real-time features that make your content dynamic and engaging. Whether you prefer coding for full control or using plugins for convenience, both methods can help you integrate external data into your website.
And by using custom fields, you can organize and display API content in a clean and structured format and then use raw data to create user-friendly and reusable content blocks.
You May Also Like:
- How to Troubleshoot WordPress Websites?
- How To Solve 500 Internal Server Error (Failed to Load Resource)
- How to Fix the ERR_ADDRESS_UNREACHABLE in Chrome
FAQs
What is the easiest way to fetch data from an API in WordPress?
Use a plugin like WPGetAPI or similar API integration tools. These plugins help you connect external APIs without custom coding. Simply enter the API URL, choose the endpoint, and display the data using a shortcode.
Do I need to write code to fetch API data in WordPress?
No, you don’t necessarily need to write code. Plugins can handle everything for you.
Can I save the API response in WordPress custom fields?
Yes. You can easily store API data inside WordPress custom fields using the update_post_meta() function. This allows you to reuse or display the same data anywhere across your website.
Will fetching API data slow down my WordPress site?
It can, if not integrated in the right way. First, you should cache API responses using WordPress caching plugins. This reduces unnecessary API requests every time a page loads, keeping it fast and responsive.
How do I securely store API keys in WordPress?
Always store API keys in your wp-config.php file or environment variables, not directly inside your theme or plugin files. This prevents them from being exposed publicly and helps keep your site secure from unauthorized access.
How often should I fetch or update API data in WordPress?
It depends on how often the source data changes. For frequently updated data (like stock prices or weather), you can use scheduled events with wp_cron to refresh the data every few minutes or hours. For static information, weekly updates are enough.
What happens if the API request fails or returns no data?
If an API request fails, the website shows a blank section or a broken layout. So, always set a fallback message or cached data. Check for errors with is_wp_error() and fix them as soon as possible.






